Induction Heating Over Other Heating Processes?
Induction heating offers several advantages over alternative methods like torch heating. Unlike torch heating, which is imprecise and relies on external heat, induction heating allows precise control of the heating location within the material using different electrical frequencies. It also enables accurate adjustments to both the width and length of the heated area, providing a level of accuracy that traditional torch-based methods cannot achieve.
Torch heating uses flammable gases, posing explosion risks, potential worker injuries, and property damage. It also emits hazardous fumes, requiring strict respiratory precautions, especially in confined spaces.
In contrast, induction heating is safer, producing no hazardous fumes when used correctly and eliminating the need for flammable gases and their associated explosion risks.
Induction heating in industrial maintenance offers faster heat treatment compared to furnace heating, which relies on electrical resistance and takes longer, especially for thick parts. Induction heating quickly heats both the surface and core, saving significant time over traditional furnace methods.
Despite the many benefits of induction heating and heat treatment, some limitations persist. Components with simple shapes, like tubes or plates, are easier to treat than complex ones. The difficulty lies in placing an induction coil around intricate shapes unless an induction furnace is used.
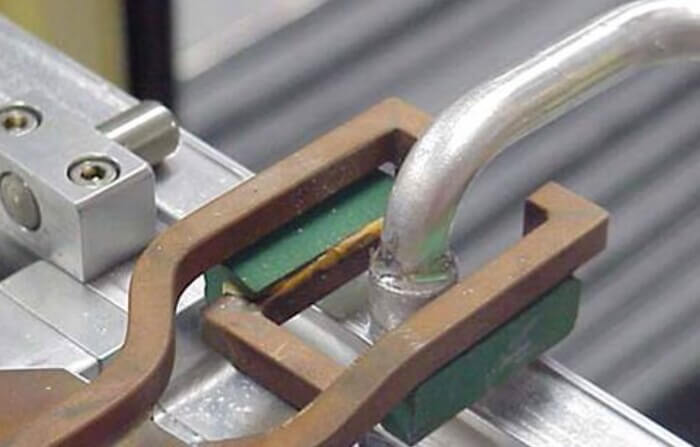
Induction Heating Equipment
The configuration for induction heat treatment of welds varies by application, but Kexin has equipment for most standard scenarios. Each induction heating system relies fundamentally on a power source, which converts electrical energy from the grid into an electric current to power the essential induction coil.
The induction coil, predominantly constructed from copper, operates without the necessity of direct contact with the workpiece. The two primary components integral to an induction system are the power source and the induction coil.
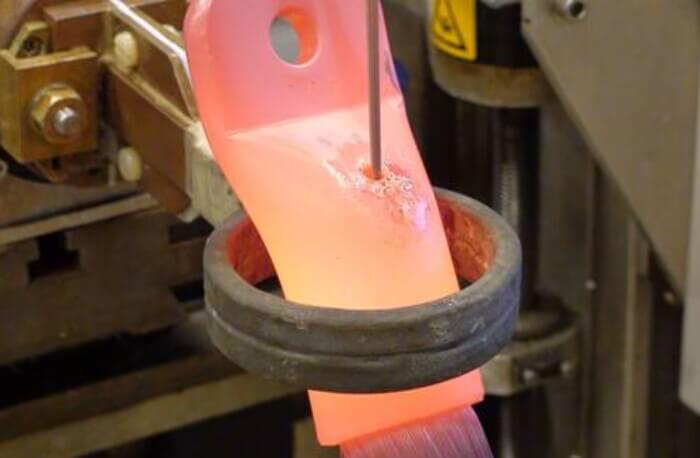

Pros of Induction Heaters
One of the main benefits of induction heaters is efficiency. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely on conduction or radiation, induction heating heats the material directly through electromagnetic induction. This results in faster heating times, lower energy consumption, and more precise temperature control.
Another benefit of induction heaters is safety. Because the heat is generated directly within the material being heated, there is less risk of fire or burns than with open flame or convection heating methods.
Induction heaters are also environmentally friendly because they do not produce harmful emissions or byproducts.
In addition, induction heaters are versatile and can be used in a variety of applications from metal processing to the food industry to medical sterilization. They are also easy to integrate into automated production lines, which can increase productivity and reduce labor costs.
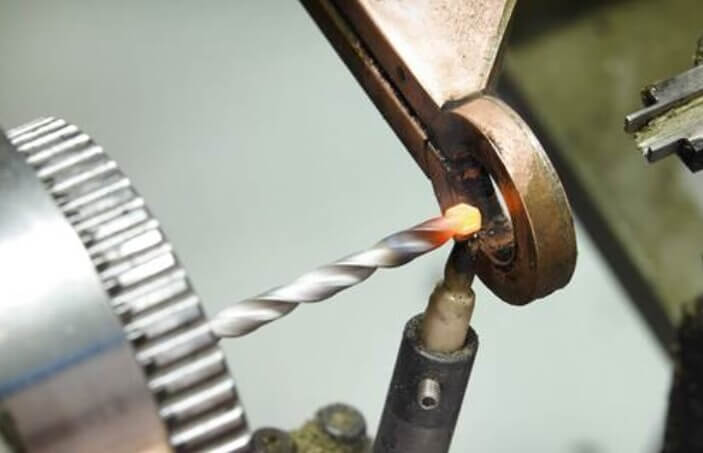

Cons of Induction Heaters
One of the main disadvantages of induction heaters is their high initial cost, as the equipment and installation can require a significant investment.
In addition, induction heaters tend to be more complex to operate and maintain than traditional heating methods and may require additional training for personnel.
Another disadvantage is that induction heating can be limited in the types of materials that can be effectively heated. Some materials, such as plastics or non-conductive materials, may not be suitable for induction heating.
In addition, the electromagnetic fields generated by induction heaters can interfere with electronic equipment and medical devices, so caution must be exercised in certain environments.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
