What Is an Induction Bearing Heater and How It Works?
An induction bearing heater is a specialized tool that uses electromagnetic induction to efficiently heat bearings. This method ensures precise installation and removal of bearings, minimizing the risk of damage. Induction heaters significantly improve industrial efficiency by preventing defects and contamination.
In industrial maintenance and machine assembly, precision and efficiency are essential. Induction heaters are subtly changing the way we install bearings. Whether you work in manufacturing, automotive, or aerospace, understanding this technology will have a significant impact on safety and productivity.
What Is an Induction Bearing Heater?
An induction bearing heater is a device that uses electromagnetic induction to heat bearings. This heating process ensures uniform expansion of the bearing, enabling precise installation or removal and preventing damage. In industrial applications, you can rely on this tool to improve bearing performance and lifespan. Induction heating eliminates the risks associated with traditional heating methods, such as uneven heating or contamination.
The growing demand for efficient bearing installation and maintenance has driven the widespread adoption of these heaters across industries. They support preventative maintenance and sustainable practices, making them indispensable tools in modern industrial environments.
The Science Behind Induction Heating
Thermal Expansion Principle: Metals expand when heated. By carefully heating a bearing, the inner ring expands to just the right size to easily fit onto the shaft. As the bearing cools, it contracts, forming a tight interference fit.
Target Temperature: Most manufacturers recommend heating bearings to approximately 230–250°F (110–120°C). This temperature is sufficient for the metal to expand for installation, but below the threshold that would alter the steel’s hardness or metallurgical structure. Some bearings and motors are designed for higher heating temperatures, but 230–250°F is the average range.
Importance of Uniform Heating: Uneven or improperly controlled heating can lead to internal stress, bearing geometry deformation, or microcracks, resulting in premature failure.
How Does an Induction Bearing Heater Work?
Basic Principle of Induction Heating
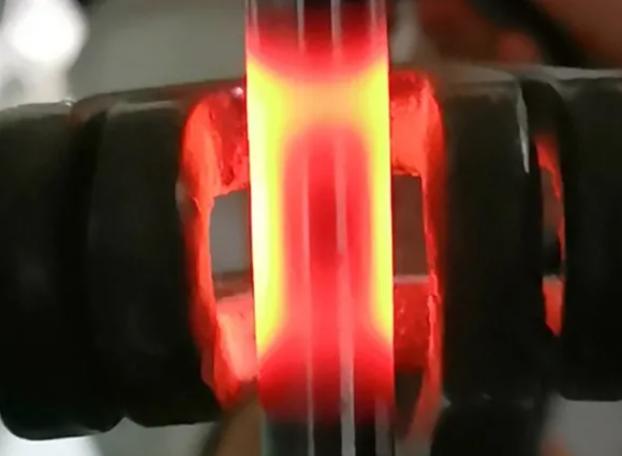
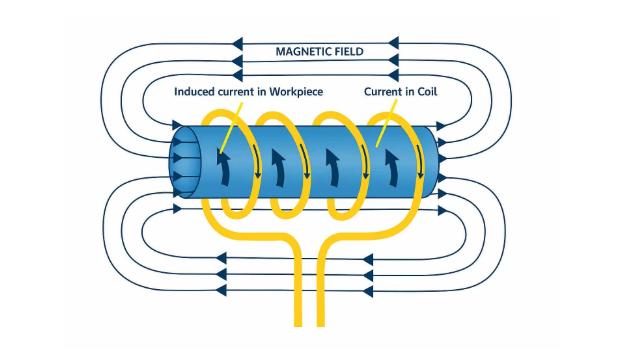
Induction heating utilizes electromagnetic energy to generate heat directly within a conductive object. When a bearing is placed in an induction heater, alternating current passes through a copper coil, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces eddy currents within the bearing, thus generating heat from the inside out.
Compared to traditional heating methods, induction heating provides faster, more controllable, and more uniform temperature distribution, significantly reducing the risk of uneven heating or material damage.
The Heating Process of a Bearing
The heating process begins with placing the bearing on a support frame or workpiece holder of the heater. Temperature probes are used to monitor the inner and outer rings of the bearing in real time. This ensures uniform heat distribution and helps prevent temperature gradients that could lead to cracks or deformation.
When the bearing reaches the target temperature, it expands sufficiently for easy installation or removal. After the process is complete, the bearing cools naturally and returns to its original dimensions, ensuring a secure fit.
One of the main advantages of induction heaters is their precision. By eliminating localized hot spots, they help maintain the structural integrity of the bearing. In practical applications, compared to traditional electric heating methods, this results in faster heating cycles, less downtime, and more consistent maintenance.
Built-in Safety and Temperature Control
Modern induction bearing heaters are designed with safety and precision in mind. Automatic temperature control systems prevent overheating, while built-in safety protection devices shut down the equipment upon detecting abnormalities.
Dual temperature sensors play a crucial role in ensuring uniform heating of the bearing’s inner and outer rings. Many systems also include automatic demagnetization, eliminating residual magnetism after heating and preventing metal particles from adhering to the bearing surface.
These features collectively make induction heaters a reliable solution for industrial environments. Precise temperature control helps protect high-value bearings from thermal stress, extending their service life and supporting safer, more reliable maintenance.
Types of Induction Bearing Heaters
Induction bearing heaters are available in a variety of designs to meet diverse application needs. Portable models are commonly used for on-site maintenance due to their ease of transport and operation. In industries such as automotive manufacturing and repair, technicians rely on these compact heaters to quickly and efficiently handle bearings.
For larger-scale or more demanding applications, stationary induction heaters offer higher heating capacity and more robust control functions, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications.
As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency, safety, and ease of use, the demand for induction bearing heaters continues to grow. The need for energy-efficient equipment and simplified maintenance processes drives continuous product development. To this end, manufacturers are increasingly adopting intelligent control and sustainable design principles to better meet the needs of modern industry.
Why Use Induction Heaters for Bearing Installation?
Accurate and Consistent Temperature Control
Induction heaters allow precise temperature settings, helping ensure bearings are heated only within safe limits. Unlike ovens, which often heat unevenly, or oil baths that are difficult to regulate, induction heating delivers consistent, repeatable results every time.
Safer and Cleaner Installation
Induction heating eliminates many of the safety and housekeeping concerns associated with traditional methods:
- No hot oil, smoke, or unpleasant fumes
- Lower risk of burns and fire hazards
- A clean, dry process with no contamination risk
This makes induction heaters especially well suited for controlled or sensitive work environments.
Faster Heating, Less Downtime
Heating a bearing in an oven or oil bath can take 30 minutes or more. With an induction heater, the same task is often completed in 5–10 minutes, or even faster. When installing multiple bearings, this time savings quickly translates into higher productivity and shorter maintenance windows.
Long-Term Cost Advantages
While induction heaters typically involve a higher initial investment, they reduce labor time, improve installation accuracy, and help extend bearing service life. Over time, these benefits often outweigh the upfront cost, resulting in lower total ownership expenses.
Better Protection for Bearings
Induction heating applies heat evenly throughout the bearing, preventing localized hot spots and unwanted changes to the steel’s microstructure. Built-in demagnetization further protects the bearing by preventing metal particles from adhering to its surface after installation.
Typical Applications and Best Practices
Although bearing installation is the most common use, induction heaters are widely used across many industries and applications:
- Motors and pumps: Installing bearings, couplings, and seals
- Gearboxes: Shrink-fitting gears and sprockets
- Heavy industry: Steel mills, mining, energy, and paper production
- OEM production lines: Ensuring repeatable, contamination-free installations
- Food and beverage processing: Clean environments where oil baths and ovens are not acceptable
- Small-scale jobs: Handheld induction heaters for nuts, bolts, couplings, and localized bearing heating
With proper temperature control and handling procedures, induction heaters offer a safe, efficient, and reliable solution for both maintenance and production environments.
How to Choose the Right Bearing Heater?
When it comes to selecting a bearing heater, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The right choice depends on your application, operating environment, and production requirements. The key factors below can help guide your decision.
Bearing Size and Type
Bearing size is one of the most important considerations. Smaller bearings, such as deep groove ball bearings, are often heated using hot plates, which provide gradual and controlled heating. For larger bearings, especially spherical or cylindrical roller bearings, induction bearing heaters are typically the preferred option due to their higher heating capacity and efficiency.
Heating Method and Speed
Different heating methods serve different needs. Induction heaters are designed for fast, controlled heating and are ideal for applications where quick mounting is required. Hot plate heaters, on the other hand, heat more slowly and are better suited for situations where gradual temperature increase is important. In high-volume or time-sensitive operations, induction heating is generally the better choice.
Application Environment
The working environment also plays a major role in heater selection. Portable induction heaters are well suited for on-site maintenance and field service, where mobility and ease of use are critical. Fixed or stationary heaters are better suited for workshops and production facilities that handle larger bearings or higher throughput.
Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption should not be overlooked. Induction bearing heaters are typically more energy-efficient than hot plate heaters, as they transfer heat directly to the bearing with minimal loss. Choosing an energy-efficient heater can help reduce operating costs, especially in continuous or high-frequency applications.
Conclusion
Using induction heaters is the best method for safe, efficient, and precise bearing installation, without causing any damage or unnecessary downtime. Kexin is committed to providing you with reliable, high-performance bearing installation equipment.
Contact us today to talk with our experts who can help you select the most suitable induction heater for your specific application, whether you are installing small precision bearings or large industrial components.
FAQ
1. What types of bearings can an induction bearing heater heat?
You can heat many types of bearings, including ball bearings, roller bearings, and cylindrical bearings. Please be sure to check the heater’s specifications to ensure it is compatible with your bearing size.
2. How to ensure safety when using an induction bearing heater?
Use the heater’s automatic temperature control and fault protection functions. Wear protective gloves and follow the manufacturer’s instructions during operation to prevent accidents.
3. Can induction bearing heaters be used for other components?
Yes, they can be used for gears, couplings, and other metal components. Ensure the component conforms to the heater’s specifications to guarantee safe and effective heating.
4. What is a bearing heater used for?
A bearing heater is a device used to heat bearings before installation and removal.
5. What is the best way to heat bearings?
The best way to heat bearings is to use a bearing heater. Bearing heaters offer advantages such as precise temperature control, suitability for bearings of various sizes, and safer operation.
6. Why heat bearings?
Bearings are installed or removed by expanding through heating, thus avoiding the need for excessive force or cold installation or removal.
KEXIN’s induction melting furnace has higher thermal efficiency and lower energy consumption. They can produce a mild metal bath mixture, mixing a uniform alloy at a constant and uniform temperature. For these reasons, this type of furnace is the first choice for induction melting. Kexin products can flexibly meet all customer requirements.
Can we help you?
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp