What Are the Advantages of Induction Heating?
Induction heating uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat within a material. It’s primarily used for heating metals but can also be applied to glass, ceramics, and semiconductors. Induction heating has several advantages over other heating methods such as convection or resistance heating, as shown below.
Energy Efficiency
This heating method shows superior energy efficiency compared to resistance heating, using less power to achieve the same thermal effect on a material. Induction heating offers up to a 50% increase in efficiency, significantly reducing energy costs.
Heats Only the Target Area
Induction heating precisely targets specific areas by generating an electromagnetic field that heats only the material’s surface, preventing heat dispersion to surrounding regions. This makes it more efficient than other methods. Tailored induction coils, with the right power and frequency, can accurately heat zones of any size without affecting adjacent areas, minimizing part deformation and improving product quality. Additional infrared temperature controls can enhance precision and oversight during the process.
Precise Heating
Induction heating technology ensures precise temperature control, allowing targeted thermal application. The electromagnetic field can heat small, specific areas to high temperatures without affecting adjacent regions. This precision makes induction heating ideal for applications needing exact heating parameters, such as in the medical industry.
Safe and Clean
Induction heating is a safe and eco-friendly thermal application method. With no open flames or hot surfaces, it is ideal for environments with flammable materials, minimizing risks. Additionally, it produces no harmful emissions, making it a greener alternative to traditional heating methods.
Pollution Free
Induction heating produces no carbon dioxide, greenhouse gases, or harmful emissions, and is noise-free. Unlike traditional methods that heat surrounding areas, induction heating confines thermal generation to the targeted workpiece, creating better working conditions and reducing environmental impact.
Fast Heating Method
Induction heating’s rapid capability is a key advantage over other methods. Its electromagnetic field swiftly increases material temperature. Additionally, the quick activation and deactivation of induction heating make it ideal for applications requiring fast thermal responses.
Portable
For many years, portability has been elusive in the heating industry. The advent of induction heating technology has changed that. Induction heating offers exceptional portability, requiring only an induction heater and a power source to start the heating process anywhere.
Top Five Benefits for Manufacturing

Various Materials
Induction heating is an adaptable technology that can effectively be applied to a diverse array of materials, including both metals and semiconductors. Its versatility serves as a significant asset across numerous applications, thereby minimizing the necessity for multiple distinct heating systems.

Longevity
Induction heating systems, distinguished by their minimal moving components compared to traditional furnaces, offer a significant advantage in terms of durability. This results in prolonged equipment lifespan, reduced maintenance expenses, and minimized operational downtime.
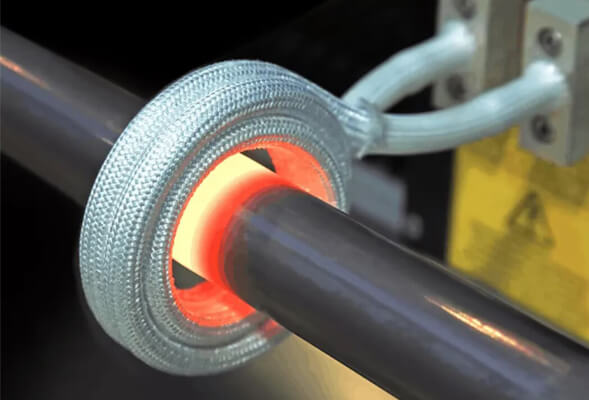
Repeatability
Induction heating provides precise temperature control and repeatability, enhancing quality control and reducing variability in manufacturing. Solid-state power sources ensure consistent heating patterns, while the non-contact nature of the induction coil and stable part positioning offer a more reliable and stable process than traditional flame or resistance heating methods.

Fast Cycle Times
Induction heating technology allows for immediate and direct heat generation within the material, maximizing heat transfer according to the material’s properties. This eliminates the long soak time seen in traditional radiant or convection heating methods.

Space Requirements and Efficiency
Induction heating technology is more space-efficient than conventional methods, making it ideal for benchtop, workshop settings, and in-line semi or fully automated processes. It is also highly energy efficient, needing minimal power for output and consuming much less energy during idle or standby modes, as it activates only during operational tasks.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
