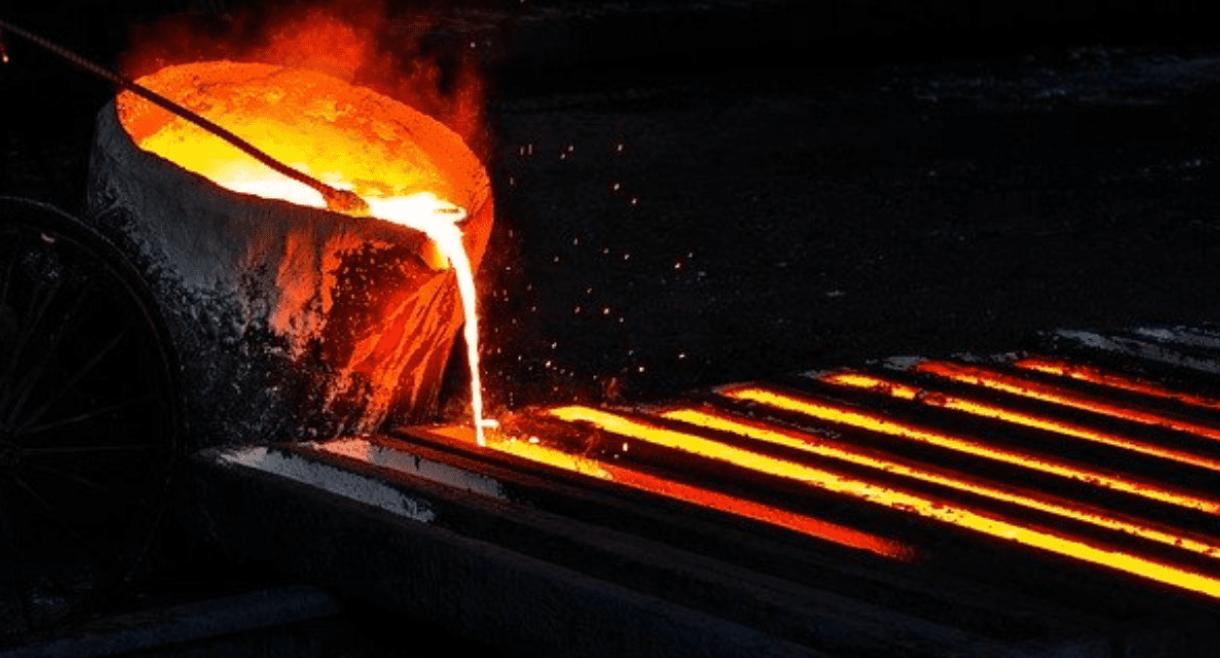
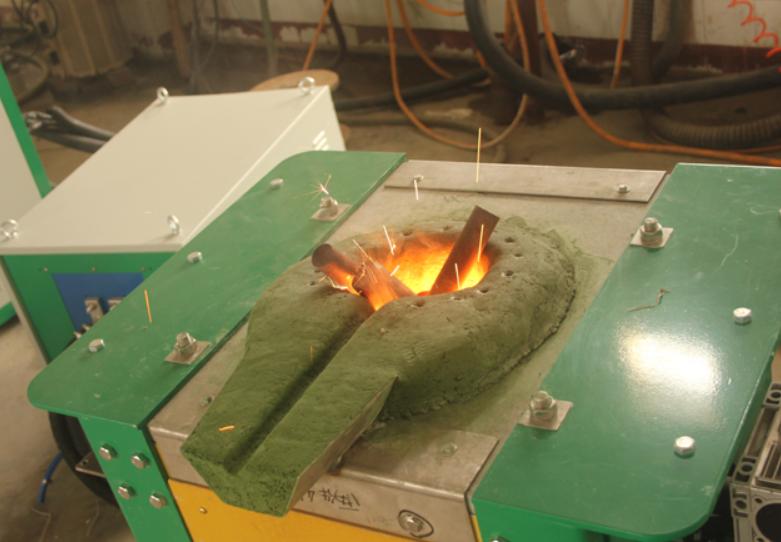
Induction Furnace for Melting Stainless Steel
Melting stainless steel is a very important industrial process. Stainless steel is a popular metal worldwide. People have been using it in a wide range of industries.
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron known for its corrosion and rust-resistant capabilities. The metal contains chromium and carbon.
Stainless steel is melted to make various products. But do you know the methods for melting stainless steel? There are several practices to melt stainless steel.
What is the Melting Point of Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is an alloy whose exact composition varies depending on the grade and intended application. It is primarily made of iron, with varying amounts of chromium, nickel, and other alloying elements.
Because of these compositional differences, stainless steel does not have a single, fixed melting point. Instead, its melting temperature falls within a range. Most stainless steel grades melt between 2,550°F and 2,790°F.
Common stainless steel grades include 301, 304, 309, 316, and 317, each with slightly different melting characteristics due to their unique alloy compositions.
Fundamental Principles of Induction Melting
Induction furnaces utilize electromagnetic induction to generate the heat needed to melt metals, including stainless steel. Their working principle is as follows: an electric current passing through a copper coil generates a magnetic field.
When a metal object is placed in this magnetic field, eddy currents are generated within the metal, causing it to heat up and eventually melt.
Medium-frequency induction furnaces are suitable for melting high-melting-point metals such as stainless steel.
These furnaces employ a fully digital control system, enabling precise melting of metals such as copper, aluminum, iron, and stainless steel. Their capacity ranges from 10 to 300 kg and can be customized to meet specific needs.
Features of medium-frequency induction furnaces include: constant power output, fast melting speed, excellent energy efficiency, and a steel shell furnace body with a hydraulic tilting design for easy melting operation.
Induction furnaces are ideal for melting stainless steel because they can quickly reach the required high temperatures, significantly reducing melting time.
Furthermore, compared to many traditional melting methods, induction furnaces offer high energy efficiency, saving costs and being more environmentally friendly.
Melting Stainless Steel in an Induction Furnace
1. Raw material preparation
Including scrap, stainless steel alloy additives, alloying elements. Remove dirt, grease and impurities on the raw materials to ensure the purity of the raw materials.
2. Loading
Load the cleaned raw materials into the induction furnace in layers according to the designed formula and proportion.
3. Turn on the medium frequency furnace
If the furnace is cold, it may need to be preheated to improve the melting efficiency. Start the induction device and turn on the power to heat, causing the current eddy current of the metal material in the furnace, so as to heat and melt it quickly.
4. Monitoring of the melting process
Temperature sensors are used to monitor the temperature of the molten metal in real time to ensure that it melts within a suitable temperature range. The metal composition can be optimized by adding alloying elements and adjusting their proportions.
5. Casting
When the metal is completely melted and reaches the predetermined temperature, the liquid metal in the furnace is poured out by tilting the furnace body or the casting port and enters the mold for molding. After casting, the metal cools in the mold to form a casting.
6. Heat dissipation and cleaning
After the casting cools to room temperature, the demolding operation is performed. Remove oxides and impurities from the surface of the casting and check the quality of the casting.
7. Post-processing
Further heat treatment, cutting and processing may be required to ensure that the final product meets the specification requirements.
Features of Induction Furnaces for Stainless Steel
Advanced Power & Start-Up Control
Seamless Soft Start: Utilizes a frequency-sweep, zero-voltage soft start mode. This allows the system to be started or stopped at any time under any condition without causing power surges or impacting the electrical grid.
Automatic Impedance Matching: Features an advanced inverter angle automatic adjustment circuit. This technology automatically manages load impedance to ensure constant power output, keeping the equipment running at peak efficiency without the need for manual capacitance adjustments.
High Efficiency & Cost-Effectiveness
Rapid Melting Cycles: Engineered for high-speed melting to significantly reduce production costs and increase throughput.
Flexible Operations: Capable of “cold starts” . The furnace can be completely emptied, making it easy to switch between different grades of stainless steel or other alloys.
Minimal Material Loss: Precise temperature control ensures uniform heating, which reduces oxidation and burning loss while maintaining a consistent metal composition.
Modern Design & User-Centric Ergonomics
Versatile Tilting Options: Available in heavy-duty steel or cast aluminum alloy shells. To suit your workflow, choose from electric, manual, or hydraulic tilting mechanisms for easy pouring.
Space-Saving Footprint: The compact design minimizes floor space requirements while maintaining high structural durability.
Sustainability & Precision
Eco-Friendly Operation: Low emission levels and reduced pollution help your facility meet strict environmental compliance standards.
Stepless Power Adjustment: Offers flexible, continuous, and smooth power regulation for precise control over the entire melting process.
How to choose the right furnace?
Choosing the right induction furnace is crucial to melting stainless steel effectively.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing an induction furnace:
Furnace Size: The size of the furnace should be appropriate for the size of the stainless steel that you want to melt. A furnace that is too small may not be able to accommodate the steel, while a furnace that is too large may waste energy.
Furnace Capacity: The capacity of the furnace determines how much steel it can melt in a single cycle. Choose a furnace with a capacity that meets your production needs.
Power Output: The power output of the furnace determines how quickly it can melt the steel. A higher power output means faster melting times.
Energy Efficiency: Choose a furnace that is energy-efficient to save on operating costs.
Conclusion
Melting stainless steel using an induction furnace is an efficient and reliable process that produces high-quality results. With the right equipment and safety precautions, it’s possible to melt stainless steel quickly and with minimal waste.
Whether you’re melting stainless steel for industrial or artisan purposes, the process requires attention to detail and a commitment to safety.
By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure that your stainless steel melting process is successful and safe. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines when operating the furnace to ensure your safety and the quality of the melt.
KEXIN’s induction melting furnace has higher thermal efficiency and lower energy consumption. They can produce a mild metal bath mixture, mixing a uniform alloy at a constant and uniform temperature. For these reasons, this type of furnace is the first choice for induction melting. Kexin products can flexibly meet all customer requirements.
Can we help you?
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp